Zookeeper概念
一、Zookeeper协调框架
1、Zookeeper是一个基于内存的分布式协调框架。其暴漏一些简单元语,基于此可以synchronization、configuration maintenance、group and naming。
2、关键特性
文件系统式结构+监听通知
3、Zookeeper设计目标
1)简单易用。提供类文件系统的内存存储结构,方便理解和使用。Java可使用Curator与ZK交互。
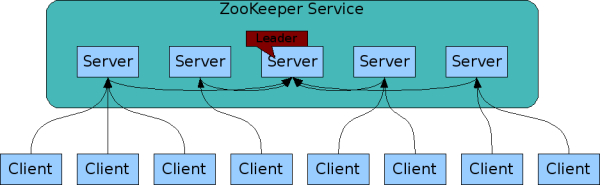
2)支持副本。一台Server故障时,客户端会自动连接到其他Server。
3)有序。Zookeeper为事务和更新提供数字标识。
4)性能好。Zookeeper在读多写少的场景下表现优异。
4、常用场景
1)分布式锁:公平锁、非公平锁、读写锁
2)注册中心:如jsf
3)Leader选举
二、一致性保证
- Sequential Consistency - Updates from a client will be applied in the order that they were sent.
- Atomicity - Updates either succeed or fail. No partial results.
- Single System Image - A client will see the same view of the service regardless of the server that it connects to. i.e., a client will never see an older view of the system even if the client fails over to a different server with the same session.
- Reliability - Once an update has been applied, it will persist from that time forward until a client overwrites the update.
- Timeliness - The clients view of the system is guaranteed to be up-to-date within a certain time bound.
三、Zookeeper持久化
1、快照
类似Redis RDB
2、事务日志
类似Redis AOF
落盘配置:
1 | // 默认强制落盘 |
四、ZAB
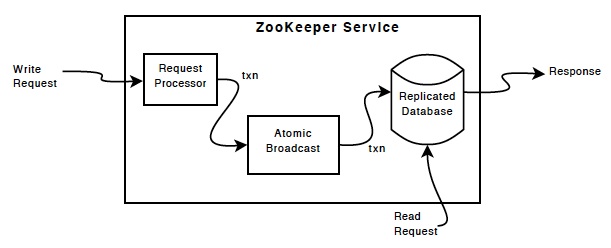
1、原子广播/崩溃恢复
2、多级队列
五、ZK集群
1、三个角色
1)leader:处理读请求,写请求
2)follower:处理读请求,可参与选举变为leader
3)observer:处理读请求
六、实现分布式锁
1、非公平锁
利用对同一个临时节点的创建和监听机制实现。容易引起羊群效应,也就是解锁时会signalAll,可使用公平锁实现方式。
2、公平锁
利用临时有序节点实现,创建临时顺序节点后,若是最小节点,获取锁;若不是最小的节点,则监听前一个节点。
3、读写锁
在公平锁基础上,对临时节点进行读写分类。读节点监听前面的写节点,写节点监听前一个写节点或者前一个写节点后的读节点。