零拷贝
零、零拷贝概念
“Zero-copy“ describes computer operations in which the CPU does not perform the task of copying data from one memory area to another. —— wikipedia
如维基百科所说,零拷贝是指避免CPU在不同的内存区域间拷贝数据。这可具体细分为操作系统级(OS level)别和用户态(User level)级别。
zero copy on OS level
针对设备驱动,文件系统,网络协议栈等内核态资源,程序可利用操作系统提供的系统函数调用,避免数据从内核态和用户态间的拷贝,充分利用操作系统资源,获得更高的性能。
具体而言,操作系统通过相应的系统函数使CPU移交总线控制权给DMA,由DMA负责内核态间数据复制操作,不通过用户态进行中转。与此同时CPU并行去处理其他复杂的逻辑,也减少了上下文切换带来的开销。
zero copy on User level
应用程序在用户态通过一些操作避免数据拷贝,也可以称为零拷贝。如Netty的CompositeByteBuf,可通过逻辑聚合多个ByteBuffer,避免物理复制多个ByteBuffer到一个大的ByteBuffer,来减少拷贝。
一、操作系统的Zero Copy
1. Linux零拷贝系统函数
sys/socket.h中的sendfile,sendfile64
splice,tee,vmsplice
process_vm_readv, process_vm_writev
copy_file_range
mmap,AF_XDP
经常有人mmap和sendfile放在一起进行比较,而忽略了他们的应用场景。
2. sendfile
1)适用场景:适用于程序不参与处理数据,数据只在系统内核态间传输
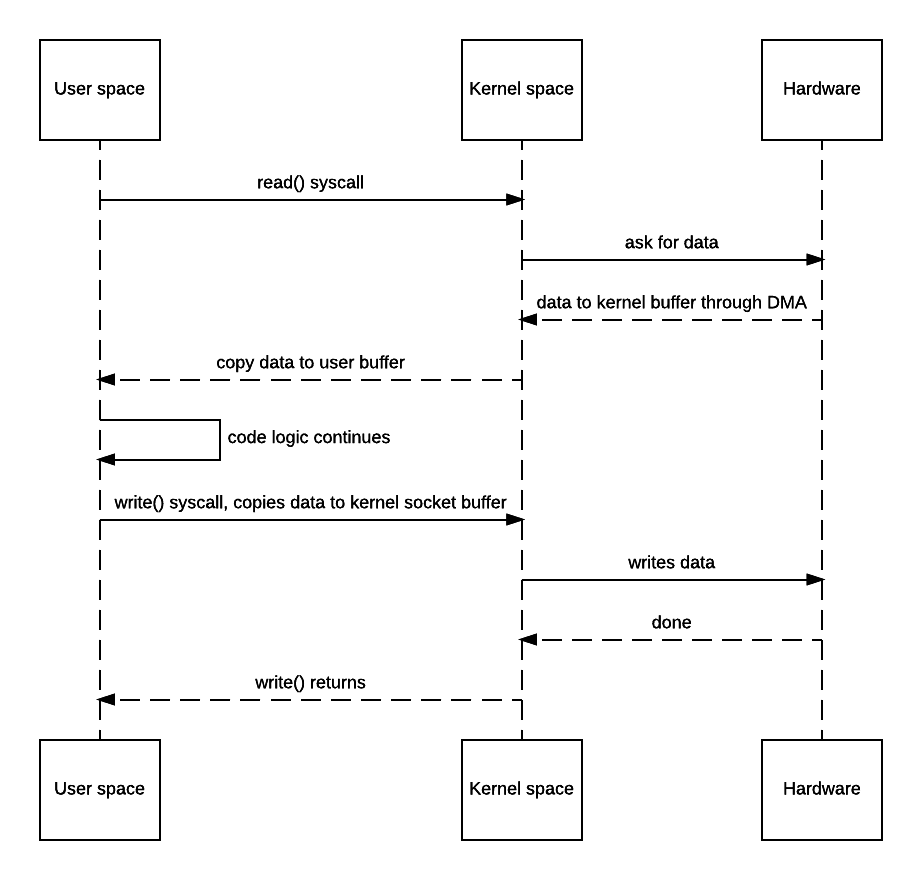
- 不使用sendfile
- 使用sendfile
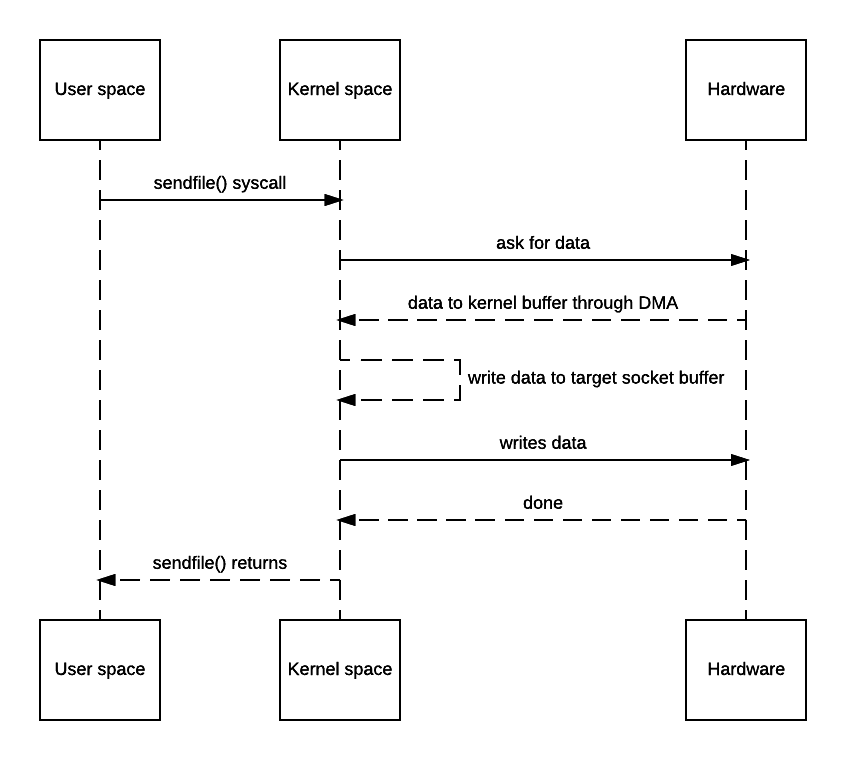
2)方法描述:由DMA负责在内核态进行数据拷贝,不再经过用户态中转
3)优点:减少了数据拷贝(内核态和用户态的拷贝为零);减少了上下文切换;对文件大小没有限制;性能更好,约比使用read,write提高65%性能。
- 不实用sendfile时,发生了4次拷贝
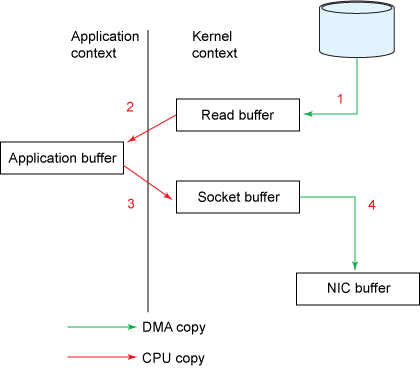
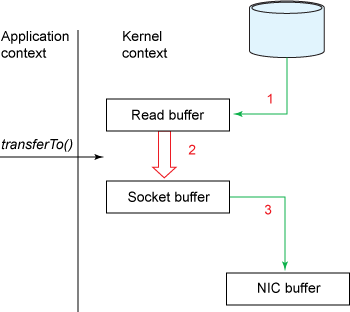
- 使用sendfile时,发生了3次拷贝,用户态拷贝为零。(如果网络接口支持gather operations,可以再减少一次拷贝: Read buffer-> Socket buffer)
- 不实用sendfile时,发生了四次上下文切换
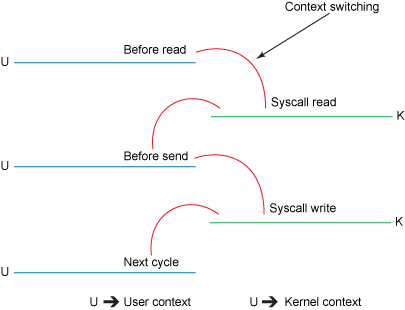
- 使用sendfile时,只有两次上下文切换
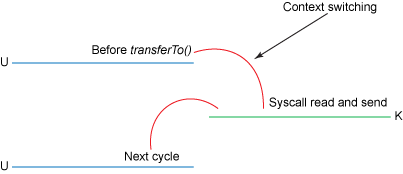
4)缺点:程序不能参与处理
3. mmap
1)适用场景:适用于程序参与处理数据,修改系统内核态的数据
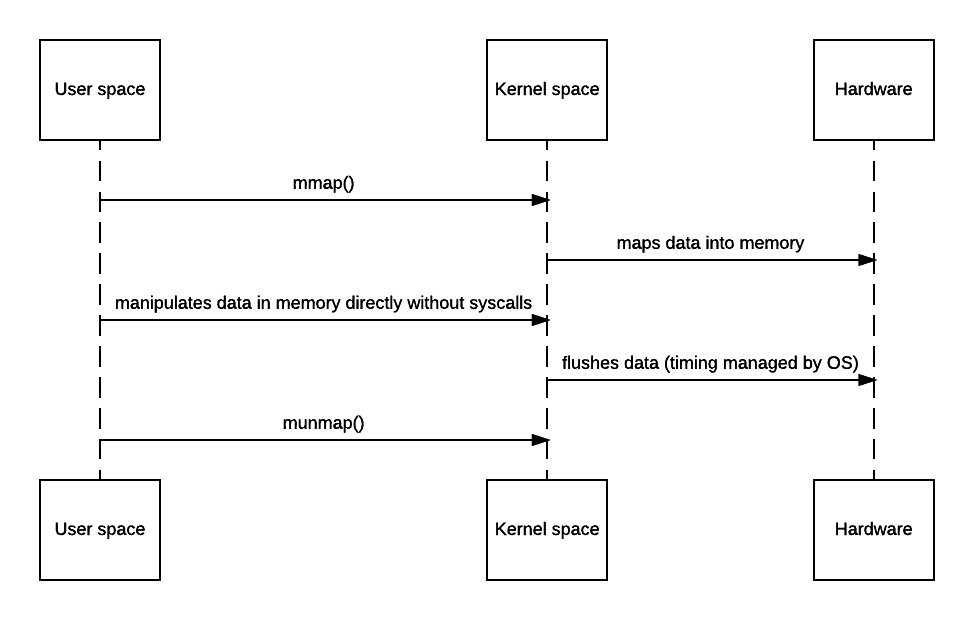
2)方法描述:把文件或设备映射到内存,他通过给定的位置读取文件对应的块到内存。用户对这块内存的修改会直接反应到内核空间,与此同时,内核空间的修改,也会直接反应到用户空间。
3)优点:程序参与处理数据;处理小文件时性能高
4)缺点:没有减少上下文切换带来的开销;处理大文件时开销较大;
4. 总结
| Sendfile | Mmap | |
|---|---|---|
| 适用场景 | 程序不处理数据 | 程序参与数据处理 |
| 上下文切换次数 | 2次 | 4次 |
| 数据拷贝次数 | 3次或2次 | 3次 |
| 文件大小与性能 | 无限制 | 小文件性能好 |
| Java NIO对系统调用的封装 | FileChannel.transferTo(long position, long count,WritableByteChannel target) | MappedByteBuffer类,可通过*FileChannel.map()*获取 |
其中,MappedByteBuffer是Java的一种direct byteBuffer。
二、Java direct vs non-direct byte buffer
直接缓冲区中通过文件映射创建的MappedByteBuffer与前面提到的mmap是一一对应的,体现了零拷贝的概念,其他类型缓冲区与OS level的零拷贝无关。
1. 直接缓冲区和非直接缓冲区的区别
The first difference between non-direct and direct byte buffer comes from the fact, how you create them. You can create non-direct byte buffer either by allocating space for buffer’s content or by wrapping an existing byte array into a buffer. While a Direct byte buffer may be created by calling factory method allocateDirect() or by mapping a region of a file directly into memory , known as MappedByteBuffer.
In the case of Direct byte buffer, JVM performs native IO operation directly into the buffer, without copying them into any intermediate buffer, this makes it very attractive for performing high-speed IO operation on them, but this facility comes with care. If a memory mapped file is shared between multiple processes then you need to ensure that it won’t get corrupted i.e. some regions of memory mapped file not becoming unavailable.
One more difference between direct and non-direct byte buffers are that former’s memory footprint may not be obvious because they are allocated outside of Java heap while non-direct buffers consume heap space and are subject to garbage collection.
You can check whether a byte buffer is direct or non-direct by calling isDirect() method from java.nio.ByteBuffer class. It returns true if byte buffer is direct.
2. ByteBuffer
如图所示,Java提供了三种ByteBuffer实现:
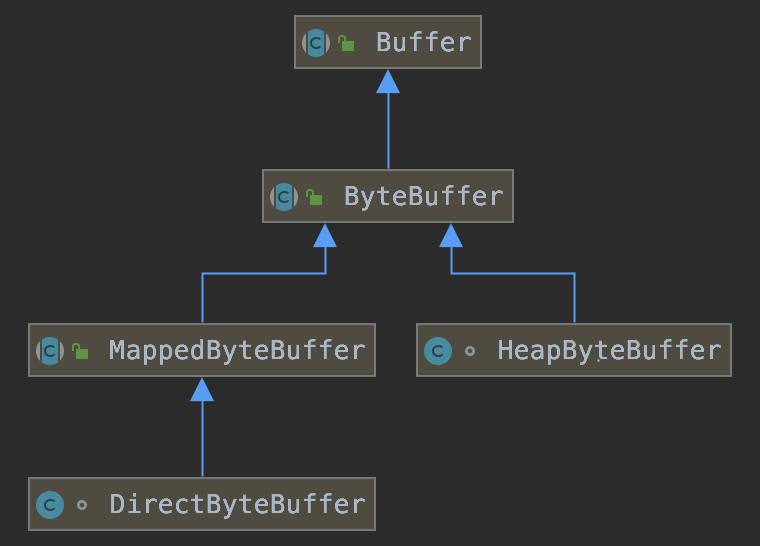
1)HeapByteBuffer
是非直接内存,用来在JVM堆上申请管理缓存,通常是字节数组的包装类。受JVM GC控制。
2)MappedByteBuffer
也是一种直接内存,是用来映射文件到直接内存中的,不受JVM GC控制。其通过系统函数mmap调用实现,利用缺页中断机制实现直接访问文件,避免数据拷贝到用户态,体现了零拷贝。
FileChannel.map最终也是调用了DirectByteBuffer的构造函数DirectByteBuffer(int cap, long addr, FileDescriptor fd, Runnable unmapper)。
3)DirectByteBuffer
是直接内存,用来在JVM堆外申请和管理内存,不受JVM GC控制。ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(int capacity)会调用构造函数DirectByteBuffer(int cap)。
1 | // Primary constructor |
三、常见Java中间件对零拷贝的使用
1)Netty
- OS-level:FileRegion封装了FileChannel.transferTo()
- User-level:
Transparent zero copy is achieved by built-in composite buffer type,类CompositeByteBuf避免了ByteBuf间的拷贝。
2)Kafka
- OS-level:Customer从broker消费数据,采用sendfile;
- OS-level:Producer生产的数据持久化到broker,采用mmap文件映射;
3)RocketMQ
- OS-level:生产和消费,采用mmap;
# 参考
- ✽It’s all about buffers: zero-copy, mmap and Java NIO
- ✽Efficient data transfer through zero copy - IBM developer
- ✽Difference between Direct, Non Direct and Mapped ByteBuffer in Java
- ✽Zero-copy - wikipedia
- ✽DirectByteBuffer and MappedByteBuffer
- Zero Copy I: User-Mode Perspective
- Netty与Zero Copy
- is-nettys-zero-copy-different-from-os-level-zero-copy
- 理解Netty中的Zero-copy
- Kafka零拷贝
- 零拷贝