文件正确写入bom
0. 什么是BOM(byte order mark, 字节序标记)?
bom可认为是unicode编码格式的一个标识。bom的字符为\uFEFF,不同编码格式下会encoding为不同的字节序,如下图: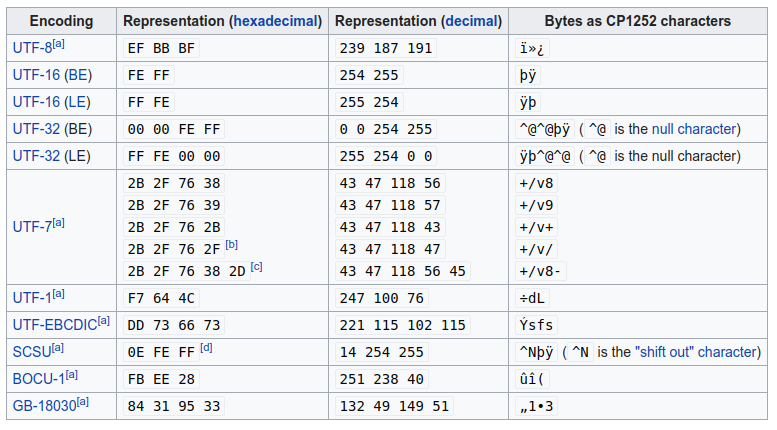
1. BOM作用
- 确定字节序,大端序 or 小端序(用于16-bit,32bit编码)
- 确定文本流为Unicode编码格式
- 确定当前使用的哪种Unicode编码格式
2. 细说UTF-8下的字节序
- String.valueOf(‘\ufeff’).getBytes(“utf-8”),得到bom在utf-8下的字节序:
0xef,0xbb,0xbf - 若某字符串起始字符为
\ufeff,则通过*String#getBytes(“utf-8”)*产生含bom的utf-8字节数组
3. Java写入Bom示例:
1)使用PrintStream#write(int i),该方法写入的是字节,即最低位字节
源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30/**
* Writes the specified byte to this stream. If the byte is a newline and
* automatic flushing is enabled then the <code>flush</code> method will be
* invoked.
*
* <p> Note that the byte is written as given; to write a character that
* will be translated according to the platform's default character
* encoding, use the <code>print(char)</code> or <code>println(char)</code>
* methods.
*
* @param b The byte to be written
* @see #print(char)
* @see #println(char)
*/
public void write(int b) {
try {
synchronized (this) {
ensureOpen();
out.write(b);
if ((b == '\n') && autoFlush)
out.flush();
}
}
catch (InterruptedIOException x) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
catch (IOException x) {
trouble = true;
}
}Demo:
1
2
3
4PrintStream out = System.out;
out.write('\ufeef'); // emits 0xef
out.write('\ufebb'); // emits 0xbb
out.write('\ufebf'); // emits 0xbf1
2
3
4PrintStream out = System.out;
out.write(0xef); // emits 0xef
out.write(0xbb); // emits 0xbb
out.write(0xbf); // emits 0xbf2)PrintStream#print(char c),
该方法写入的char。源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/**
* Prints a character. The character is translated into one or more bytes
* according to the platform's default character encoding, and these bytes
* are written in exactly the manner of the
* <code>{@link #write(int)}</code> method.
*
* @param c The <code>char</code> to be printed
*/
public void print(char c) {
write(String.valueOf(c));
}Demo
1
2PrintStream out = System.out;
out.print('\ufeff');3)StringWriter.write(int c),
写入的是char,同PrintStream#print。源码
1
2
3
4
5
6/**
* Write a single character.
*/
public void write(int c) {
buf.append((char) c);
}